CLAIMS
1. A method of diagnosing and treating a sacroiliac joint of a patient, the method comprising:
a) delivering a first member into the ilium via a first posterior approach;
b) delivering a second member into the sacrum via a second posterior approach, the second member not crossing the sacroiliac joint;
c) coupling the first and second members to a pliers; and
d) manipulating the first member in the ilium relative to the second member in the sacrum via the pliers.
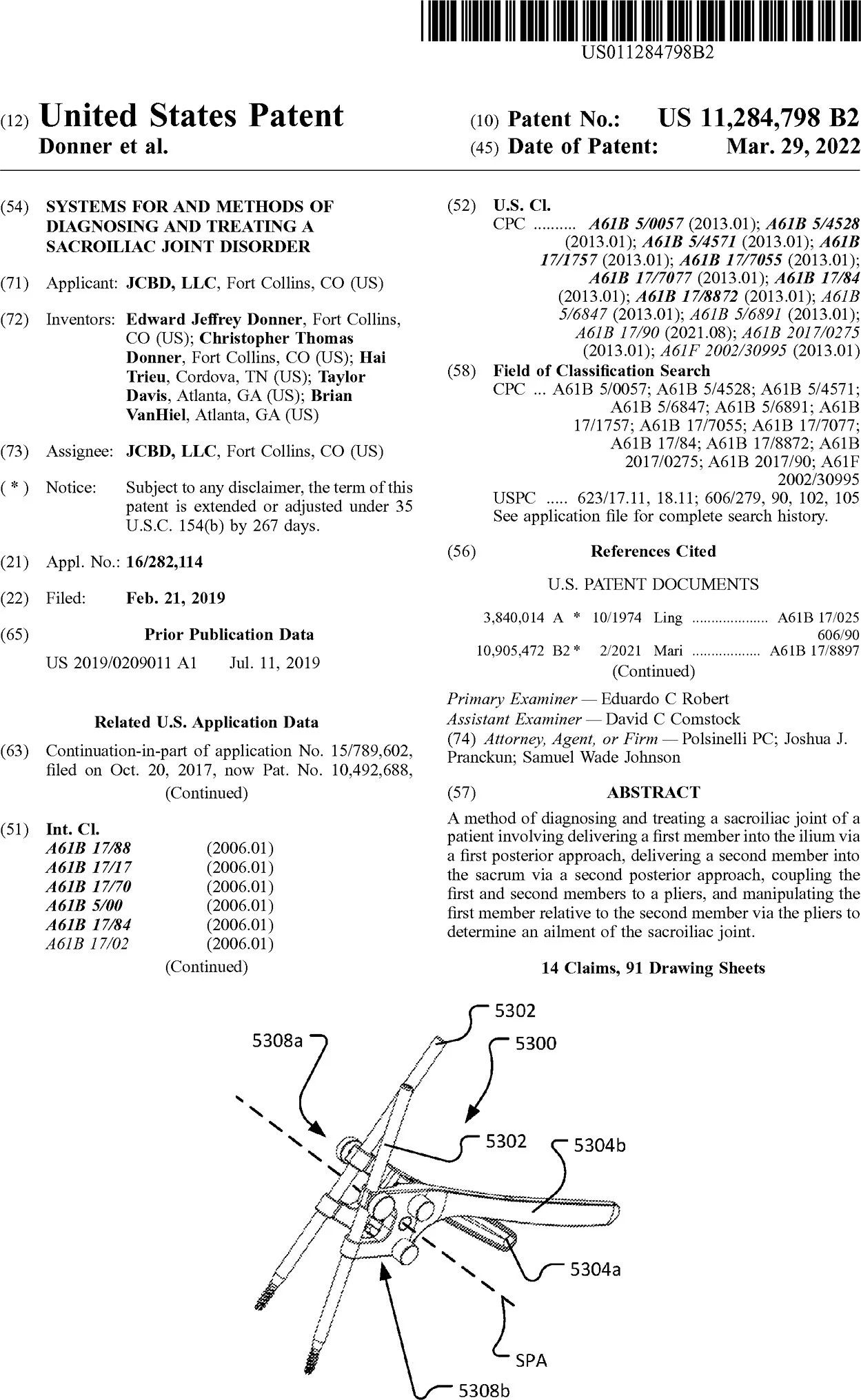
2. The method of claim 1, wherein the pliers are a dual-axis pliers comprising first and second handles, first and second head portions, and a pair of joints adjustably coupling the first and second handles and the first and second head portions, the pair of joints facilitating rotation of the first and second head portions about first and second axes, wherein the first and second axes are generally perpendicular to each other.
3. The method of claim 1, wherein the pliers comprise first and second handles, first and second head portions, and a first joint adjustably coupling the first and second handles and the first and second head portions, wherein the pliers are expanding pliers such that movement of the first and second handles closer together via rotation about a first axis of the first joint causes the first and second head portions to move apart from each other.
4. The method of claim 3, wherein the pliers further comprise a second joint adjustably coupling the first and second handles and the first and second head portions, wherein the second joint facilitates rotation of the first and second head portions about a second axis of the second joint, the second axis being generally perpendicular to the first axis.
5. The method of claim 4, wherein the pliers further comprise at least one stud member configured to be engaged and disengaged with the first joint, wherein engagement of the stud member with the first joint limits rotation of the pliers to the first axis of the first joint, and wherein disengagement of the stud member with the first joint permits rotation of the pliers to the first axis of the first joint and the second axis of the second joint.
6. The method of claim 1, further comprising: e) receiving feedback from the patient including whether or not manipulating the first member relative to the second member via the pliers at least one of reproduces, stimulates, and alleviates a symptom being investigated.
7. The method of claim 1, wherein the pliers comprise at least one of an analog and a digital readout.
8. A method of diagnosing and treating a sacroiliac joint of a patient, the method comprising:
a) delivering a first member into the sacrum via a first posterior approach;
b) sliding a first dilator over the first member;
c) sliding a sleeve of a first guide of a parallel pin guide over the first dilator;
d) positioning a second guide of the parallel pin guide so as to target the ilium;
e) inserting a second dilator into the second guide; and
f) delivering a second member into the ilium via guidance by the second dilator.
9. The method of claim 8, wherein the first and second members are guide wires, and the method further comprises delivering first and second bone pins, respectively into the locations of the first and second members.
10. The method of claim 9, further comprising manipulating the first and second bone pins relative to each other.
11. The method of claim 10, further comprising using at least one of a pliers and a clevis guide to manipulate the first and second bone pins relative to each other.
12. The method of claim 8, further comprising inserting a pair of radiographic contrasting members into radiographic guide holes of the parallel pin guide, and aligning the radiographic contrasting members with the sacroiliac joint.
13. The method of claim 12, wherein aligning the radiographic contrasting members with the sacroiliac joint is done under radiographic imaging.
14. The method of claim 12, wherein aligning the radiographic contrasting members with the sacroiliac joint causes the second guide of the parallel pin guide to target the ilium.